»Getting Started with Waypoint
It only takes a few minutes to get started with Waypoint on your local development environment. This quick start example uses Docker, either on Linux or with Docker Desktop for Windows and macOS.
Afterwards, go in-depth with tutorials for AWS, Azure, GCP, Kubernetes, and Nomad at HashiCorp Learn.
»Installing Waypoint
Download the Waypoint binary and install it to your system. The
easiest way to install it is to use our official signed packages for Homebrew,
apt, yum, and other package managers.
»Installing the Server
Start the Docker Desktop application.
Pull the hashicorp/waypoint Docker image.
$ docker pull hashicorp/waypoint:latest
Install the Waypoint server to Docker with the install command. The
-accept-tos flag is required to use the waypoint.run URL publishing service.
$ waypoint install --platform=docker -accept-tos
When it completes, you'll see this message.
✓ Server container started
Waypoint server successfully installed and configured!
The CLI has been configured to connect to the server automatically. This
connection information is saved in the CLI context named "install-1601411904".
Use the "waypoint context" CLI to manage CLI contexts.
The server has been configured to advertise the following address for
entrypoint communications. This must be a reachable address for all your
deployments. If this is incorrect, manually set it using the CLI command
"waypoint server config-set".
Advertise Address: waypoint-server:9701
HTTP UI Address: localhost:9702
»Initializing Waypoint
Clone the git repository with Waypoint application examples, or download the code directly from GitHub.
$ git clone https://github.com/hashicorp/waypoint-examples.git
Navigate to the docker/nodejs directory.
$ cd waypoint-examples/docker/nodejs
All the code you need is provided in this directory, including a waypoint.hcl
configuration file that will deploy the application to Docker.
Run init to set up the project.
$ waypoint init
You'll see this output.
✓ Configuration file appears valid
✓ Local mode initialized successfully
✓ Project "example-nodejs" and all apps are registered with the server.
✓ Plugins loaded and configured successfully
✓ Authentication requirements appear satisfied.
Project initialized!
You may now call 'waypoint up' to deploy your project or
commands such as 'waypoint build' to perform steps individually.
»Deploying
Now, run waypoint up to build, deploy, and release the application.
$ waypoint up
It may take a minute or two and then you'll see this output.
» Building...
✓ Creating pack client
✓ Building image
✓ Injecting entrypoint binary to image
Generated new Docker image: example-nodejs:latest
» Deploying...
✓ Setting up waypoint network
✓ Starting container
⠹ App deployed as container: example-nodejs-01EMM4TEN9SCXXE900F4EFQ9NR
» Releasing...
The deploy was successful! A Waypoint deployment URL is shown below. This
can be used internally to check your deployment and is not meant for external
traffic. You can manage this hostname using "waypoint hostname."
URL: https://instantly-worthy-shrew.alpha.waypoint.run
Deployment URL: https://instantly-worthy-shrew--v1.waypoint.run
Visit either URL shown in the output. You will see a NodeJS application running on your local Docker Desktop instance.

»Changing
Change any part of the file at docker/nodejs/views/pages/index.ejs such as
the <h1> tag at about line 18. Run up again to deploy a new version of the
application.
$ waypoint up
You'll see a new URL that you can visit to view the latest version of the application.
»Debugging
Waypoint includes several sub-commands to help you monitor and debug your application.
Run logs to view Waypoint's logs. This may not include all of your
application-specific logs, but will display Waypoint's logs.
waypoint logs
The exec command connects you to a running instance of your application where
you can examine the process list, run application-specific database upgrade
commands, or do other debugging.
waypoint exec bash
# ps aux
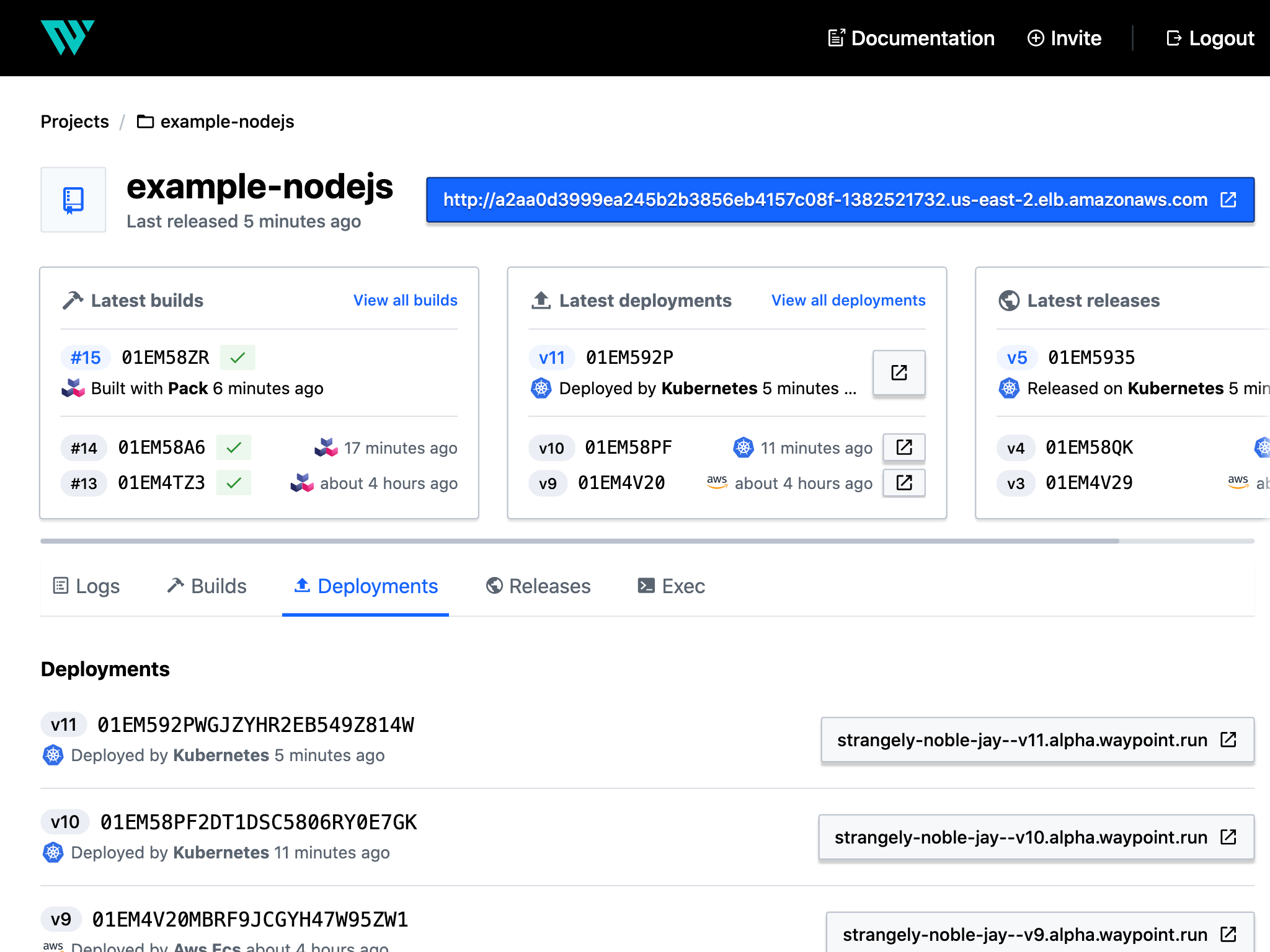
»Viewing the Web UI
Waypoint includes a web interface for viewing logs, deployments, builds, and
other details. Launch it with the ui command.
waypoint ui -authenticate
»Destroy
When you are done, run destroy to remove the application from Docker.
$ waypoint destroy
»Next Steps
You have used Waypoint to build, deploy, and release a NodeJS application to Docker.
For more detailed examples in many programming languages and on real cloud resources hosted at AWS, Azure, and GCP, visit HashiCorp Learn.